Protein (PDB-101)
from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protein
- A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide.
- Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides.
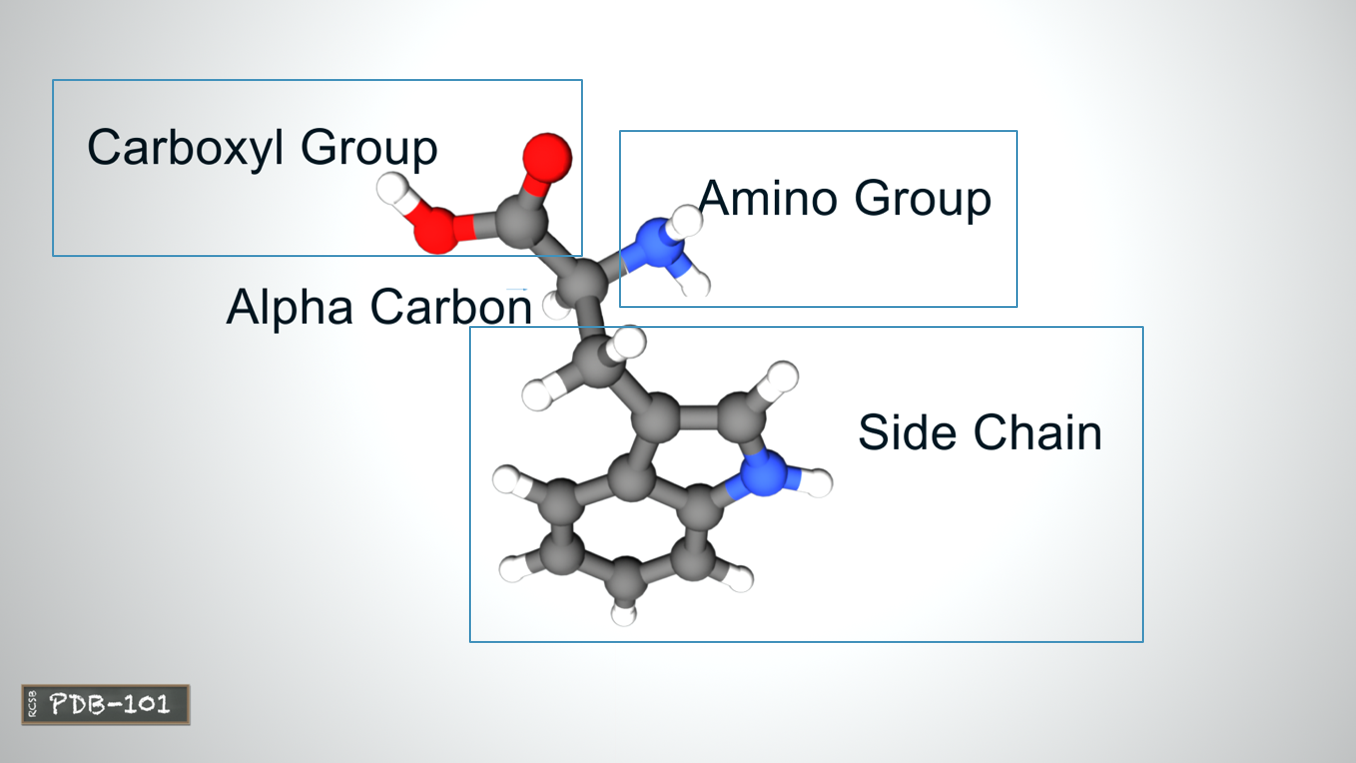
- The amino acids in a polypeptide chain are linked by peptide bonds between amino (-NH2) and carboxyl group (-COOH).
- An individual amino acid in a chain is called a residue.
- A polypeptide chain ends with a free amino group, known as the N-terminus or amino terminus, and a free carboxyl group, known as the C-terminus or carboxy terminus
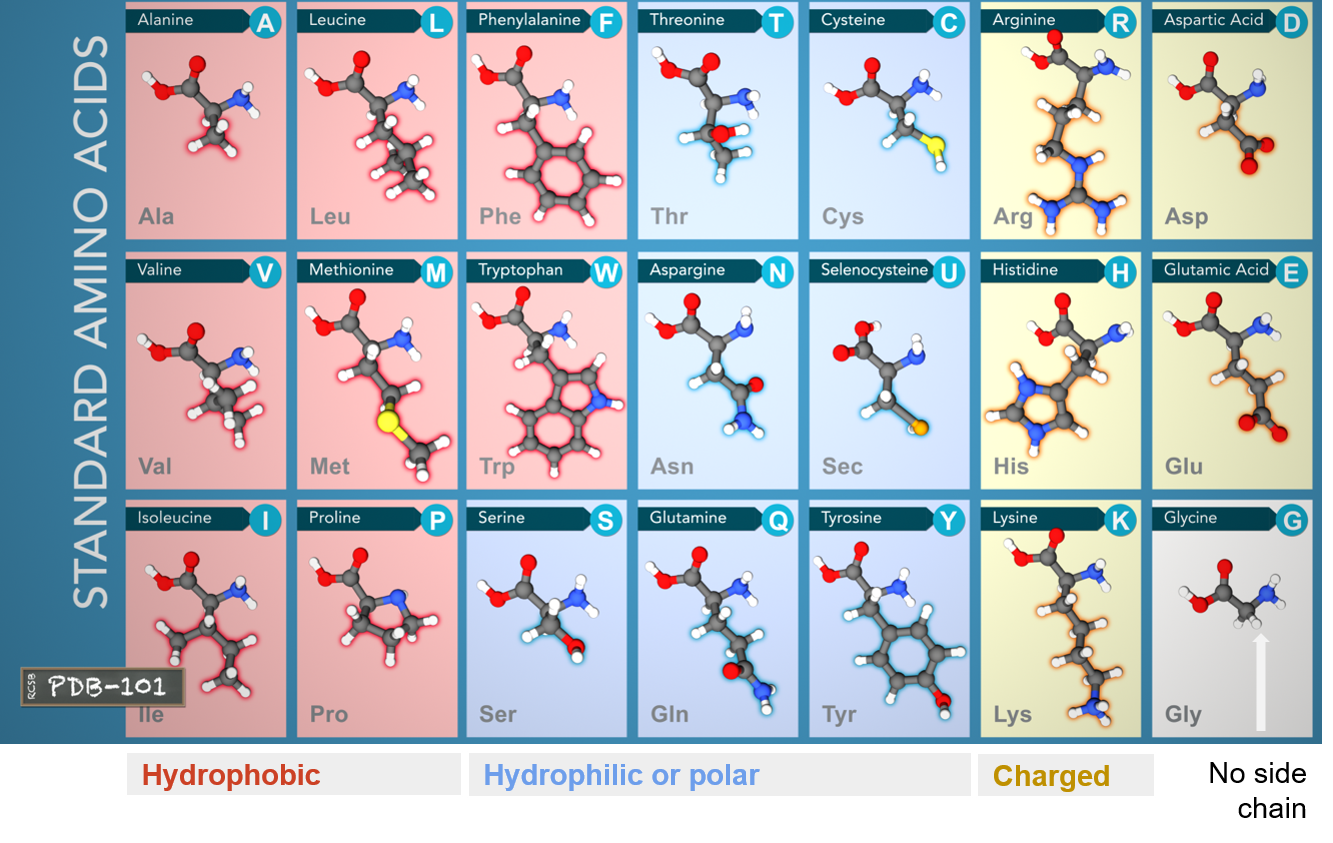
All proteins are made of 21 amino acids.
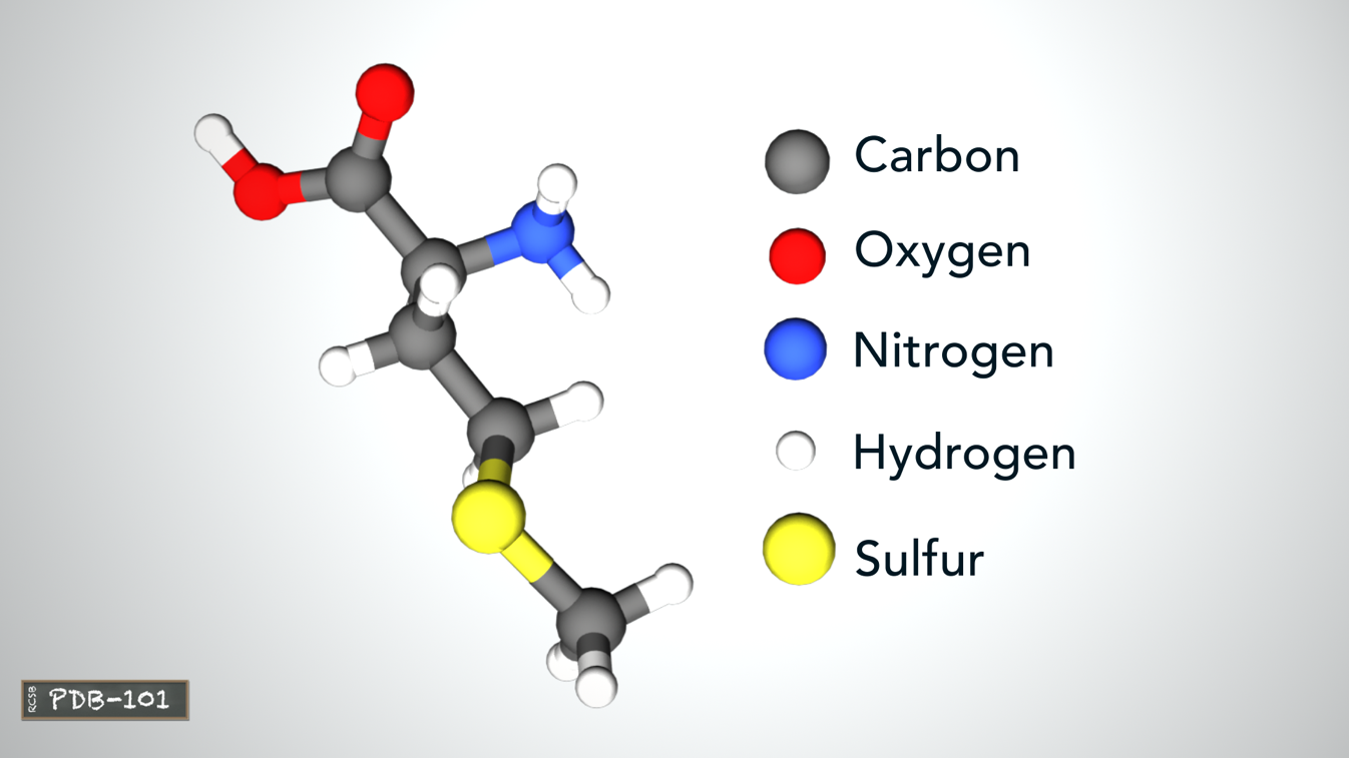
Each amino acide is made of Carbon, Oxyden, Nitrogen, Hydrogen atoms. And some have sulfur atoms too.
These amino acids can be divided into three groups based on their properties determnined by their side chains:
- Hydrophobic: carbon-rich side chains which don't interact well with water.
- Hydrophilic/Polar: iteract well with water.
- Charged: iteract with oppositely charded amino acids or other molecules.
Structure
Primart structure
Linear sequence of amino acids encoded by DNA
Amino acids are joined by peptide bonds, happending between -COOH and -NH2. A water H2O molecule is released each time a bond is formed.
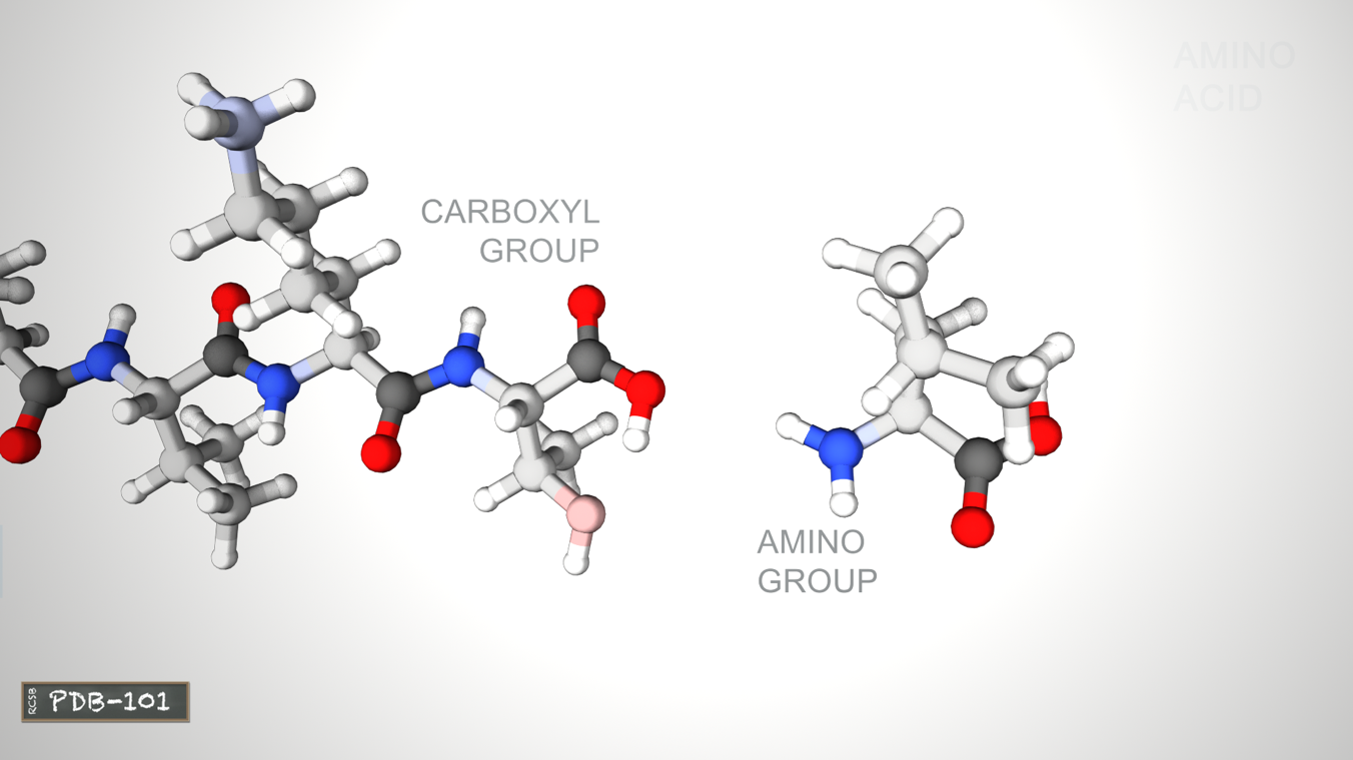
The linked series of carbon, nitrogen and oxygen atoms make up the protein backbone
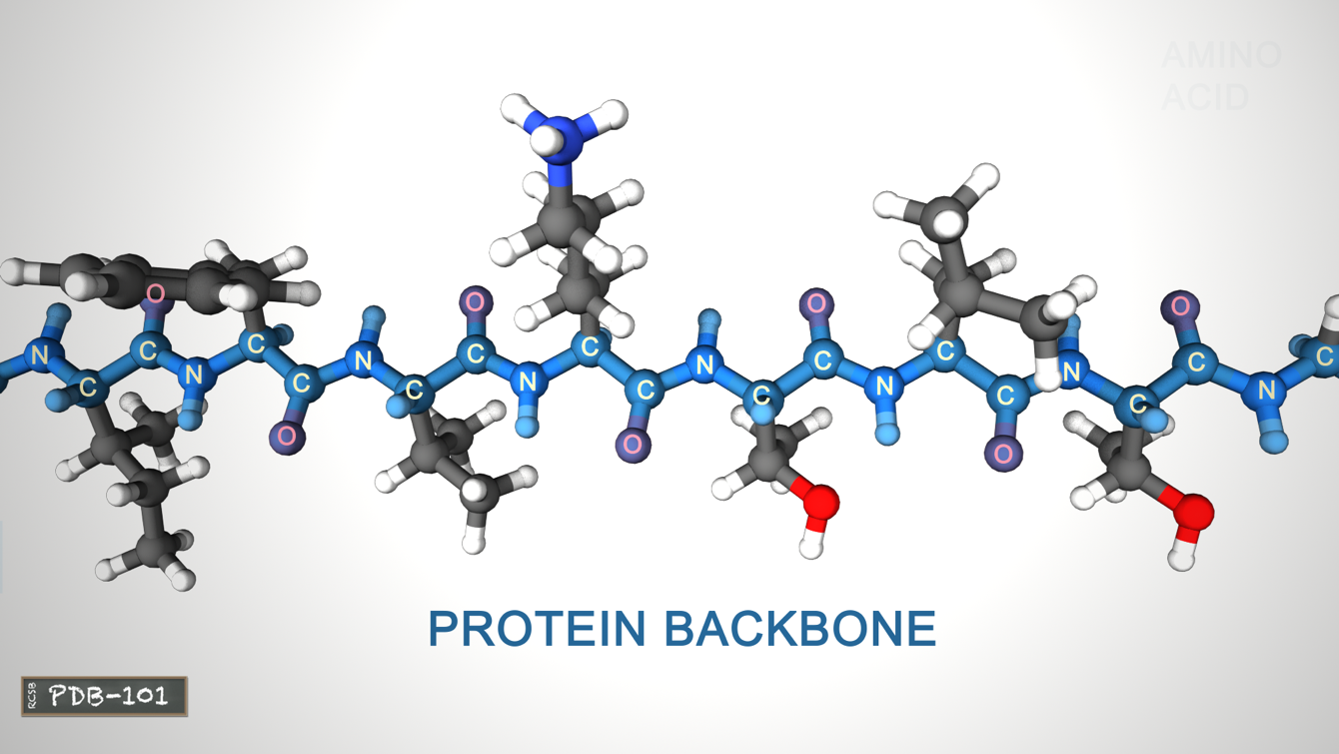
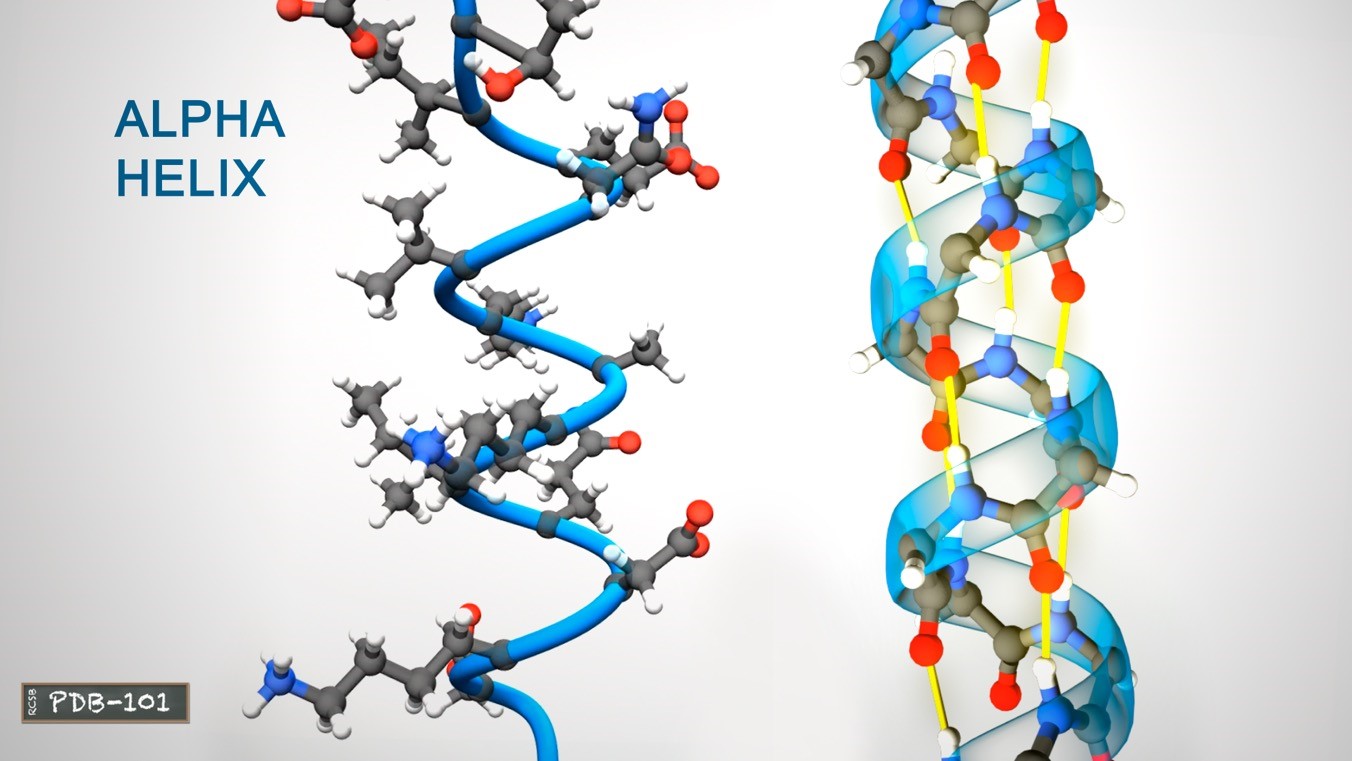
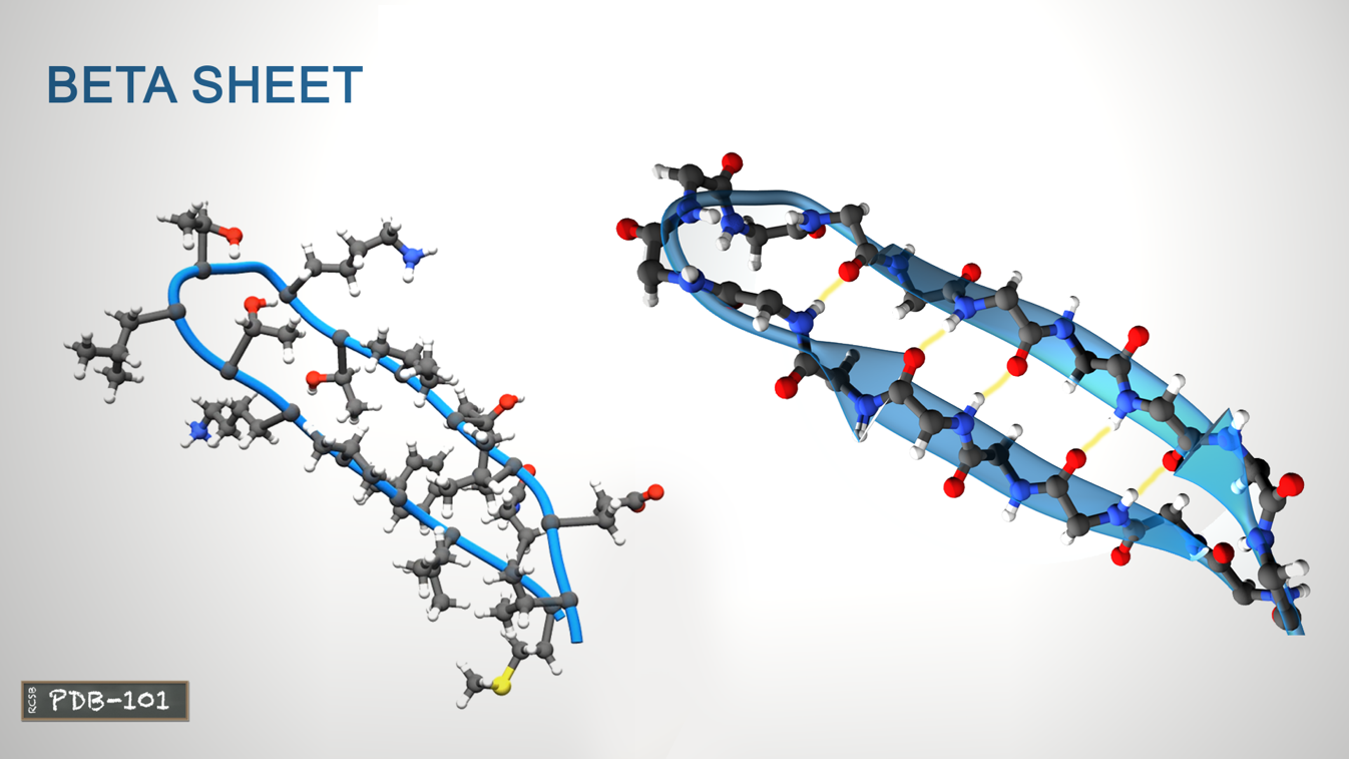
Secondary structure
Alpha helix and Beta sheet

Tertiary structure
3D shape of the protein
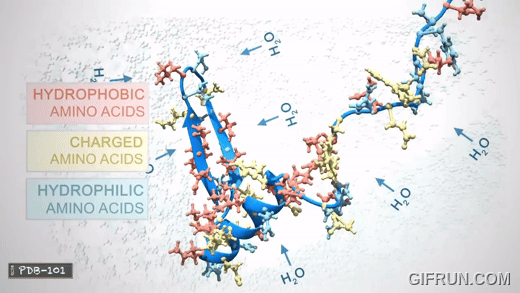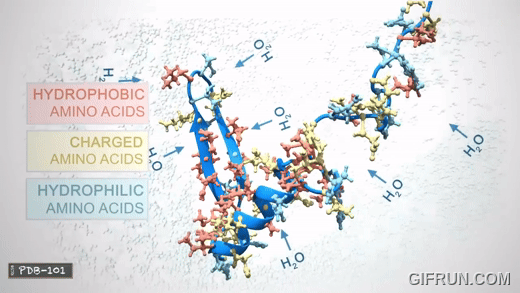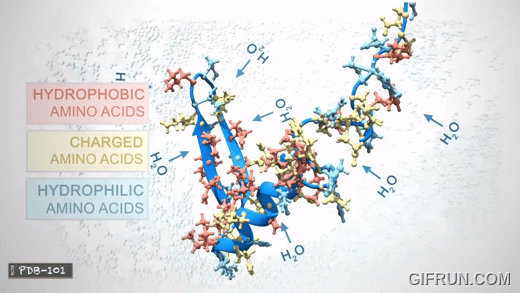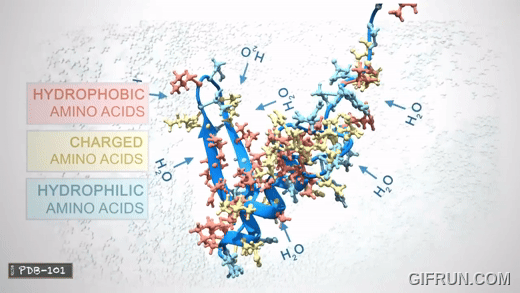
Quaternary structure
Two or more polypeptide chains come together to form one fucntional molecule wih several subunits.